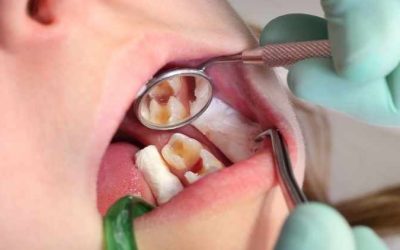
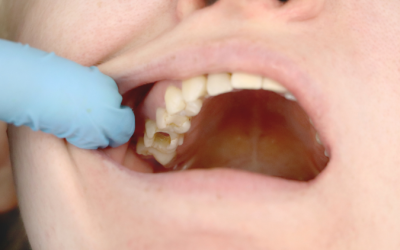
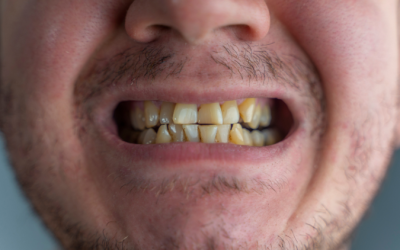
Cavities are one of the most common dental issues people face. They form when bacteria in your mouth produce acids that erode the enamel, creating tiny holes in your teeth. Spotting a cavity early can prevent more serious dental problems and help maintain your oral...
Dental Insights
What Does a Cavity Look Like? Recognizing Early Signs of Tooth Decay
Cavities, or dental caries, are among the most common oral health issues. They develop when plaque bacteria produce acids that erode your tooth enamel. Recognizing the early signs of a cavity can help you seek timely treatment and prevent more serious dental problems....
Best Toothpaste for Receding Gums: Protecting Your Oral Health
Gum recession is a common dental concern that affects many adults. It happens when the gum tissue surrounding your teeth wears away, exposing the roots. This can lead to tooth sensitivity, pain, and an increased risk of gum disease. One simple way to protect your gums...
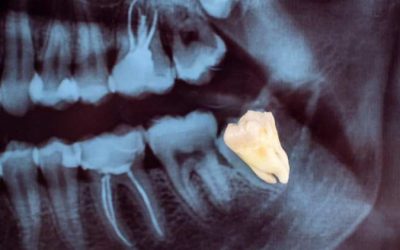
What Does Wisdom Teeth Pain Feel Like? Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
Wisdom teeth, or third molars, are the last teeth to emerge in your mouth, usually appearing between the ages of 17 and 25. While some people’s wisdom teeth grow in smoothly, others experience pain and discomfort that can disrupt daily life. Understanding what wisdom...
What Are the White Spots on My Teeth? Causes and How to Treat Them
Have you ever noticed white spots on your teeth and wondered what they mean? While they may seem harmless, white spots can indicate underlying dental issues or the effects of previous habits. Understanding the causes and available treatments can help you maintain a...
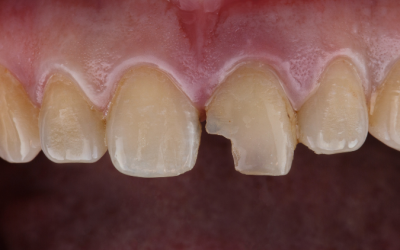
How to Fix a Chipped Tooth: Treatment Options and Steps to Take
Chipping a tooth can be alarming, but there are several effective ways to fix it. Whether it’s a minor chip or a more substantial break, immediate action and proper treatment can restore your smile and protect your dental health. In this guide, we’ll discuss how to...
How to Protect Your Teeth from Nighttime Grinding (Bruxism)
If you wake up with sore jaws, a headache, or notice your teeth are more sensitive than usual, you might be grinding your teeth at night. Known as bruxism, nighttime teeth grinding is common and can have lasting effects on your dental health. Understanding bruxism and...
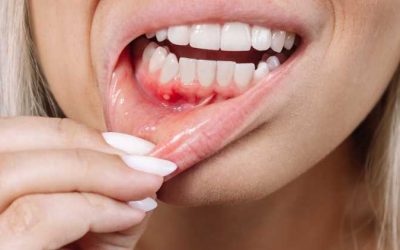
My Gums Won’t Stop Bleeding: Causes and Solutions
If you’ve noticed that your gums won’t stop bleeding, you’re not alone. Bleeding gums are a common issue that many people experience at some point. While it may seem like a minor problem, persistent gum bleeding can be a sign of something more serious and should not...
The Connection Between Oral Health and Heart Disease
Did you know that the health of your mouth can affect the health of your heart? While we often think of oral health and heart health as separate, growing evidence shows that taking care of your teeth and gums can play a role in reducing your risk for heart disease. In...
Why Do I Have Bad Breath Even After Brushing?
Brushing your teeth twice a day is one of the most effective ways to maintain fresh breath and good oral hygiene. But what happens when you’re still struggling with bad breath, even after brushing regularly? It can be frustrating and embarrassing, but the good news is...
Anatomy of A Tooth Explained
Understanding the anatomy of a tooth is key to maintaining good oral health. Each part of a tooth has a specific function, and knowing how these components work together can help you take better care of your smile. In this blog, we'll break down the basic structure of...
How Often Should I Replace My Toothbrush?
Your toothbrush plays a crucial role in keeping your teeth and gums healthy, but how often should you be replacing it? While many of us focus on brushing twice a day, we often forget that using an old or worn-out toothbrush can be less effective. In this blog, we’ll...
Why Do I Only Have Two Wisdom Teeth?
Wisdom teeth are a common topic of discussion when it comes to dental health, especially during the late teens and early adulthood when they usually emerge. While most people expect to have four wisdom teeth, some discover that they have fewer—sometimes just two. If...
What Are Peg Laterals?
Have you ever noticed that some teeth appear smaller or oddly shaped compared to others? These dental anomalies can sometimes be peg laterals. In this blog, we’ll explore what peg laterals are, their causes, how to identify and treat them, and their impact on your...
What Foods Stain Teeth?
A bright, white smile is something many of us strive for, but sometimes our favorite foods and drinks can get in the way. Tooth discoloration can impact your confidence and make you self-conscious about your smile. This blog aims to inform you about the common foods...
How Many Adult Teeth Should I Have?
Ever wondered exactly how many teeth an adult has? Understanding the anatomy of our mouths can help us take better care of our oral health. In this blog, we'll explore the number of teeth in an adult mouth, the different types of teeth, and their functions. Basic...
What Happens If I Don’t Get My Wisdom Teeth Out?
Wondering what happens if you don't get your wisdom teeth out? Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, often emerge in late adolescence or early adulthood. While many people have these teeth removed, you might wonder what happens if you don't get your wisdom teeth...
How Long Does A Bite Adjustment Take?
A properly aligned bite is essential for maintaining optimal dental health and overall well-being. However, issues such as bite misalignment can lead to various dental problems, including tooth wear, jaw pain, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders. If you're...
Why Is There A Black Spot On My Tooth?
Have you ever noticed a mysterious black spot on one of your teeth and wondered what could be causing it? Black spots on teeth can be concerning, but understanding their potential causes is essential for addressing them effectively. In this blog, we'll explore the...
What Causes Cavities?
Cavities, also known as dental caries or tooth decay, are one of the most common dental problems affecting people of all ages worldwide. Understanding the underlying causes of cavities is crucial for effective prevention and maintaining optimal dental health. In this...
When Do I Need A Mouthguard?
Mouthguards are essential tools in protecting dental health and preventing injuries to the mouth and jaw. From sports activities to sleep disorders, mouthguards play a crucial role in safeguarding our oral structures. In this blog, we'll explore the various situations...
How Many Teeth Do Adults Have?
One common question that often arises is: How many teeth do adults have? Understanding the anatomy of our teeth is fundamental to maintaining good oral health. Let's explore the answer to this question and delve into the significance of adult teeth in dental health....
Understanding TMJ Disorder: Signs and Treatment Options
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorder is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Despite its prevalence, many individuals may not be aware of the signs and symptoms of TMJ disorder or the available treatment options. In this blog, we'll explore...
Understanding the Importance of Regular Dental Checkups
Regular dental checkups are essential for maintaining good oral health and preventing dental problems. This blog explores why routine visits to the dentist are crucial and what patients can expect during these appointments. Preventative Care and Early Detection:...
What Causes Bad Breath and How Can I Combat It?
Bad breath, or halitosis, can be a persistent and embarrassing issue for many individuals. This blog aims to explore the various causes of bad breath and offer practical advice from dental professionals on how to combat it effectively. Identifying the Causes of Bad...
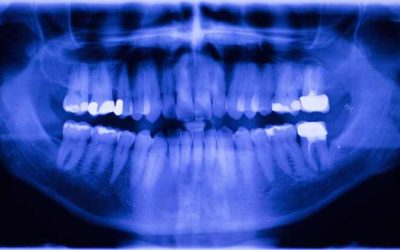
Why Do I Need Dental X-Rays? The Importance and Safety of Dental X-Rays
Dental x-rays, despite being a routine part of dental care, often raise questions about their necessity and safety. In this blog, we'll delve into why dental x-rays are crucial for diagnosing oral health issues and address common concerns regarding radiation exposure....
Smile-Friendly New Year’s Resolutions: Prioritizing Your Oral Well-being
Welcome to a brand new year filled with possibilities! As we embark on this journey, it's the perfect time to reflect on our habits and set some smile-friendly New Year's resolutions. This blog will guide you through simple and achievable goals to prioritize your oral...
The Importance of Tongue Health: A Guide to a Clean and Healthy Tongue
When it comes to oral health, the tongue often takes a back seat to teeth and gums. However, its role is far more significant than we might think. In this blog, we'll dive into the importance of tongue health and share practical tips for maintaining a clean and...
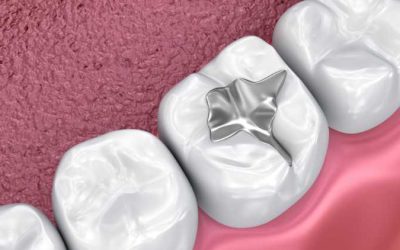
Understanding the Different Types of Tooth Fillings: A Comprehensive Guide
Today, we're diving into a crucial aspect of oral care: tooth fillings. These tiny dental superheroes play a significant role in preventing and treating tooth decay, but not all fillings are created equal. Let's explore the diverse world of tooth fillings, understand...
Maintaining Oral Hygiene While Traveling This Holiday Season
Fellow travelers and oral health enthusiasts! We all know the excitement of exploring new places, but it's crucial not to neglect our pearly whites while on the road. In this guide, we'll share practical tips on how to maintain excellent oral hygiene habits even when...